Ground Based Navigation Aids - Recommendations Released
GROUND BASED NAVIGATION AIDS
In taking advantage of the availability of the Global Positioning System (GPS), many countries have taken the opportunity to reduce the number of ground based navigation aids (GBNA) (beacons).
In New Zealand, a strategy was produced under the New Southern Sky programme that led to the formation of a GBNA Review Panel (GBNARP) in early 2017. The Panel provided recommendations on the Minimum Operating Network (MON) to safely recover IFR aircraft if GPS signals were lost. It also provided recommendations on the Contingency Network that will keep the Main Trunk (Auckland/Wellington/Christchurch) operating in the event of GPS failure.
The recommendations (in this briefing given to the NSS Working Group) were passed on to Airways on 20 December 2017.
GBNARP Recommendations
Recommendation 1.
The minimum operating network (MON) of GBNAs, to safely recover aircraft if GNSS services are lost, should comprise:
a) GBNAs at all controlled aerodromes, which will provide signal coverage for most of the country,
b) A GBNA at Kaitaia to provide signal coverage for Northland and into the Oceanic FIR,
c) A GBNA at Hokitika to provide signal coverage for the West Coast of the South Island
d) A GBNA on Chatham Island to allow aircraft to be recovered to the Chatham Islands.
Recommendation 2.
By 2020, all GBNAs in the MON should be VORs.
Recommendation 3.
The GBNAs that make up the MON should all have co-located DMEs.
Recommendation 4.
The GBNA contingency network, to enable main trunk services to continue, and to provide security and resilience backup, in case of GNSS outage, will be adequately provided by the recommended MON.
GBNA Coverage
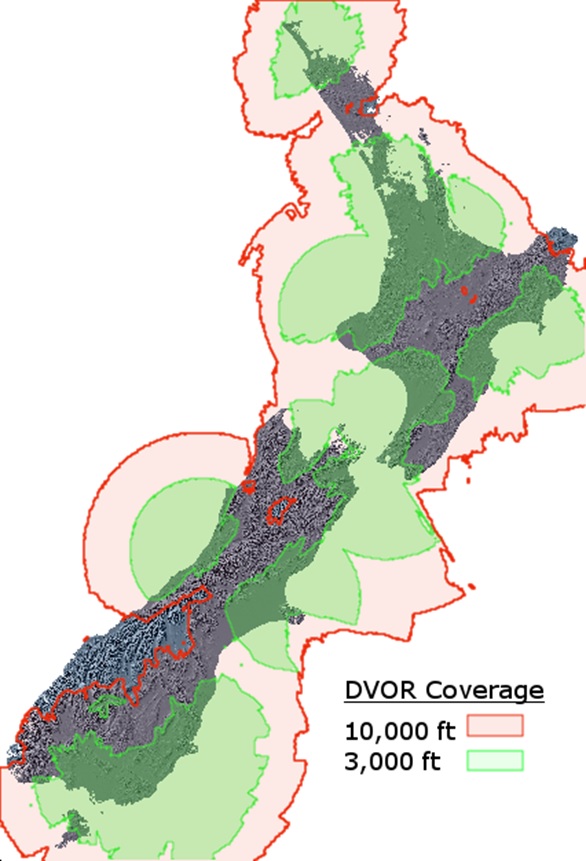
GBNA Coverage as per the recommendations of the GBNARP.